Boiler scale remains one of the most persistent and costly problems faced by industrial facilities today. As minerals from boiler water deposit onto heat transfer surfaces, they form insulating layers that reduce efficiency, increase fuel consumption, and strain critical equipment. Within any boiler system, this scale buildup can disrupt temperature regulation, compromise safety, and lead to expensive downtime. Traditional water treatment methods often rely on heavy chemical use to manage these issues, but the industry is shifting toward smarter, more sustainable solutions. By understanding the chemistry of scale and adopting advanced control strategies, facility teams can reduce waste, extend equipment life, and maintain system performance without compromising reliability or environmental responsibility.
The Science Behind Boiler Scale
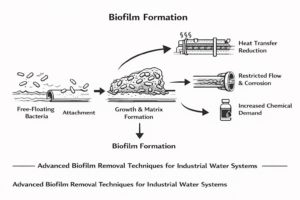
Boiler scale forms when scale-forming minerals in feedwater, such as calcium, magnesium, and silica, precipitate out under heat and pressure. As the boiler water evaporates to generate steam, the concentration of these dissolved solids increases. When the water can no longer hold these minerals in solution, they form scale on metal surfaces like boiler tubes and heat transfer surfaces.
The most common type of deposit is calcium carbonate, which crystallizes on heated areas where water hardness and alkalinity are high. Over time, these deposits grow into dense, insulating layers that block heat transfer, leading to uneven temperatures and reduced efficiency. In steam boilers, where pressure and temperature ranges are higher, the reaction occurs faster, accelerating scale formation and increasing the risk of overheating or tube failure.
Because each boiler system and water source has unique chemistry, understanding which minerals and impurities drive deposit buildup is essential. Regular analysis of feedwater composition helps determine the most effective treatment approach to prevent boiler scale, ensuring optimal heat exchange and longer equipment lifespan.
Reducing Chemical Load While Preventing Scale Buildup
Modern water treatment approaches focus on preventing scale without relying on excessive chemicals. Instead of constant overfeeding of inhibitors, today’s advanced programs use targeted chemistry, continuous monitoring, and smarter process control. By understanding water hardness, alkalinity, and other factors influencing scale formation, facility teams can tailor treatments that protect systems while minimizing waste.
Technologies such as water softeners, filtration, and remote monitoring tools allow operators to maintain consistent water quality and detect impurities before they form scale. These methods prevent boiler scale by keeping calcium and magnesium in solution rather than allowing them to deposit on metal surfaces. Continuous analysis of boiler water parameters helps technicians adjust chemical feed rates only when necessary, ensuring the system remains within the optimal operating range.
Smart chemistry also involves using polymeric or phosphonate-based inhibitors that control dissolved solids and limit crystal growth. By focusing on efficiency, detection, and monitor-based feedback, facilities can reduce total chemical consumption and achieve better results with fewer resources. This integrated solution supports safer operation, lower maintenance cost, and longer equipment life—all while helping organizations meet environmental and compliance goals.
Also read: Scale Removal Techniques for Optimal Equipment Performance
Practical Maintenance and Inspection Strategies in Boiler Water
Even the best chemical program cannot succeed without consistent maintenance and inspection. Proper procedures allow the boiler operator to identify early signs of scale formation and address them before serious damage occurs. Regular observation of tubes, pressure levels, and deposits helps prevent costly downtime and equipment failure.
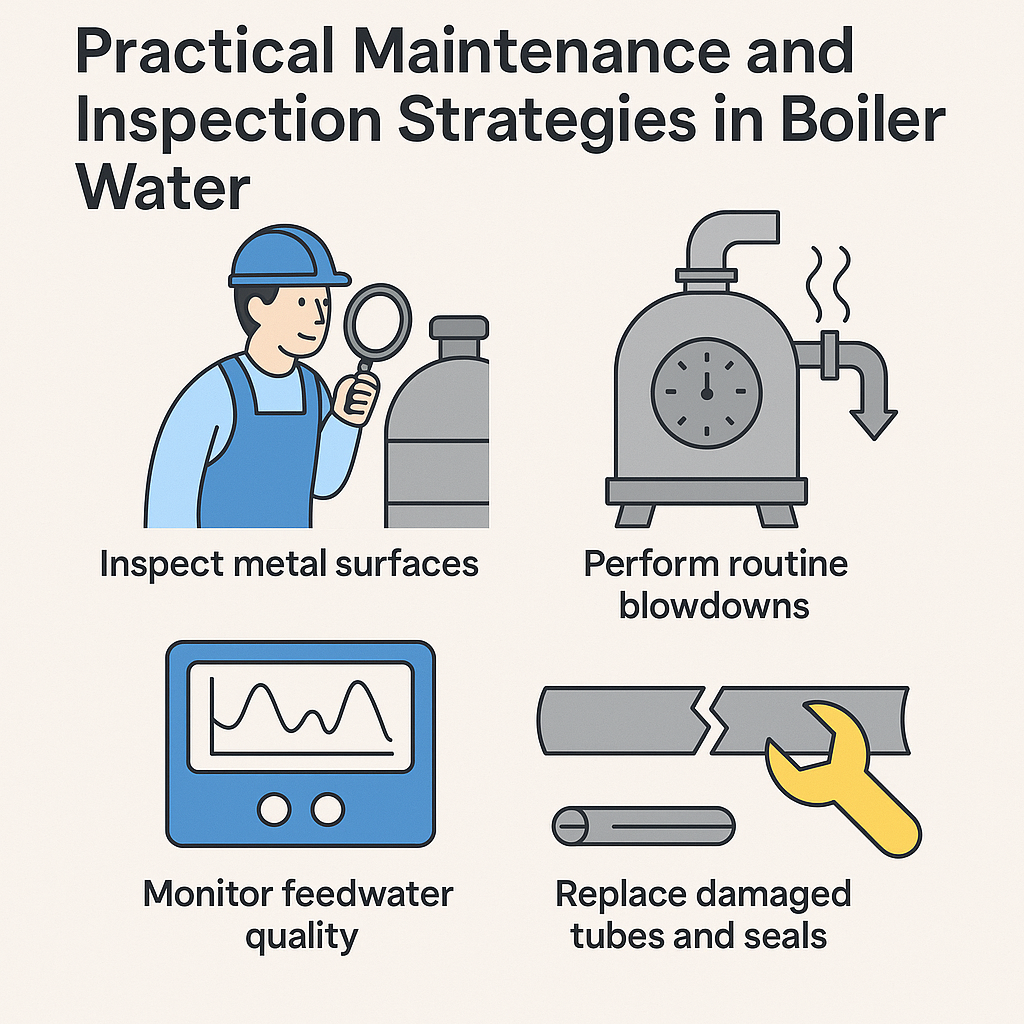
To keep your boiler system in top condition:
- Inspect metal surfaces regularly. During scheduled inspections, examine boiler tubes, welds, and walls for discoloration, scaling, or pitting on steel and other materials. These early warning signs indicate scale buildup or corrosion that can restrict flow and reduce heat transfer efficiency.
- Perform routine blowdowns. Controlled discharge of water inside the boiler helps flush solids, impurities, and dissolved minerals before they can settle and form scale. Blowdowns also maintain optimal pressure and chemical balance in the system.
- Monitor feedwater quality. Frequent analysis of alkalinity, salts, and dissolved solids allows teams to detect variations that promote formation of calcium carbonate, silica, and other deposits. This proactive step supports consistent chemical control.
- Schedule chemical cleaning when needed. When deposits are detected, approved descaling agents such as hydrochloric acid can safely dissolve layers of hardened scale under controlled procedures and temperature ranges.
- Replace damaged tubes and seals. If excessive scaling or corrosion occurs, promptly replacing affected materials helps maintain safety, performance, and efficiency over time.
Effective inspections and documentation help maintain operational stability, reduce risks, and prevent unplanned shutdowns.
ETI’s Approach to Smarter Scale Control
Effective boiler scale control requires chemistry that works intelligently within the boiler system, not against it. ETI specializes in blending advanced chemical formulations that dissolve existing deposits, prevent scale formation, and maintain heat transfer efficiency without unnecessary chemical load. Our goal is to help operators reduce waste, extend equipment lifespan, and achieve dependable system performance with minimal environmental impact.
Smarter Chemistry, Proven Results
- Customized Formulations: ETI tailors each blend to your water profile, addressing calcium, magnesium, silica, and other scale-forming minerals common in boiler water.
- Integrated System Protection: Beyond scale prevention, ETI solutions safeguard metal surfaces, boiler tubes, and feedwater circuits against corrosion, reducing downtime and operational costs.
- Advanced Cleaning Solutions: For facilities facing heavy deposits, ETI’s Water Scale Remover efficiently dissolves hardened calcium carbonate and iron deposits, restoring proper flow and heat transfer.
- Comprehensive Corrosion Control: To defend against oxidation and pitting, our Rust Treatment for Boilers protects high-temperature boiler materials, extending service life and ensuring stable pressure operation.
- Ongoing Support: Each program includes on-site analysis, product adjustments, and continuous monitoring to maintain peak system efficiency.
Partner with ETI
ETI has been a trusted partner in industrial water treatment since 1986, helping facilities in Pennsylvania and Ohio implement sustainable, chemistry-driven solutions. By combining innovation, precision, and decades of field experience, ETI empowers water treatment professionals to prevent scale buildup, reduce chemical usage, and protect their systems for the long term.
Contact ETI today or visit us to learn how our custom chemical blends can transform your boiler’s performance and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What causes boiler scale to form on metal surfaces?
Boiler scale develops when hard water containing calcium, magnesium, and silica is heated, leaving salts, solids, and other impurities that attach to steel or iron walls. Over time, these elements combine to create dense layers that block efficient heat transfer.
How can I monitor dissolved solids in my boiler water?
Routine water analysis and monitoring of dissolved solids, alkalinity, and hardness help operators detect rising mineral concentrations. Early detection allows timely adjustments to prevent additional layer formation and maintain safe operating conditions.
Why are minerals like calcium and silica such a concern?
These materials form hard, insulating deposits on heat transfer surfaces, forcing the system to use more energy and fuel. If left untreated, scale can lead to overheating, corrosion, and reduced boiler lifespan.
What methods can help prevent scale buildup in a steam boiler?
Using water softeners, chemical inhibitors, and proper blowdown procedures are effective ways to prevent scale buildup. Regular inspections ensure scale formation does not occur and equipment remains efficient.