In today’s industrial and environmental landscape, efficiency, sustainability, and precise control are no longer optional. Systems in industries ranging from HVAC and manufacturing to medical devices rely on dependable processes to deliver the desired output while conserving resources and reducing waste. One concept at the center of these goals is the closed loop system.
Understanding what is a closed loop system is essential for engineers, operators, and sustainability managers seeking to optimize performance while minimizing environmental impact. Unlike an open loop system, which runs without feedback, a closed loop system incorporates sensors, controllers, and feedback to maintain accurate control of variables like temperature, speed, or flow.
This article explores what a closed loop system is, how it differs from open loop systems, and why multi-function products are crucial for maintaining these systems.
What is a Closed Loop System?
At its core, a closed loop system is a type of control system that continuously monitors its output and adjusts its input to maintain the desired output. This dynamic process ensures accurate control over a variable, such as temperature, speed, or pressure, by responding to real-time conditions.
In a closed loop, the system uses a sensor to measure the actual value of the output. This measurement is compared against the reference input, which represents the target or set point. Any difference between the actual value and the desired output generates a feedback signal. This signal informs the controller, which then takes corrective control action to bring the system back in line with the set point.
This process creates a feedback loop, a hallmark of closed loop control systems. Because of this feedback, the system can automatically correct deviations without requiring constant human intervention.
An example of a closed loop feedback system is a heating system in a building. The thermostat (controller) compares the actual temperature (from a sensor) with the set point (desired output). If the temperature drops below the set point, the heating system increases heat output to restore balance.
Key elements of a closed loop system include:
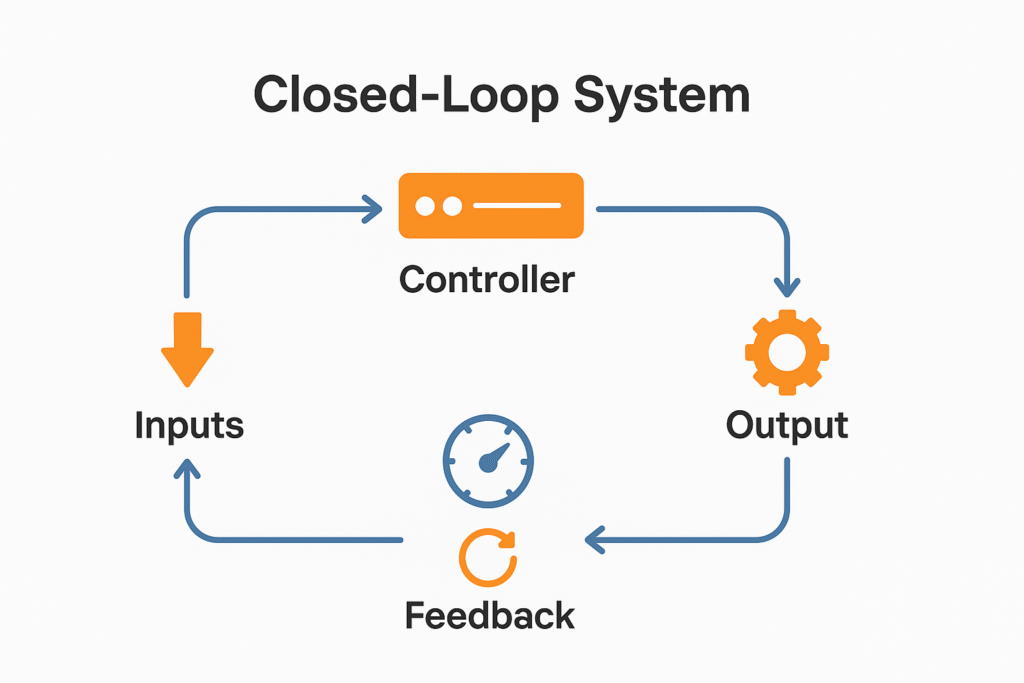
- Inputs: external signals or materials that start the process.
- Controller: device or mechanism making decisions based on feedback.
- Sensor: measures the actual value of the output.
- Feedback: information on the current output.
- Output: the result or product of the process.
This configuration allows for optimal performance, accurate control, and efficient use of resources in industrial applications, medical devices, and other sectors.
Open Loop vs. Closed Loop Systems
To fully understand what is a closed loop system, it helps to compare it with an open loop system, which operates without feedback.
An open loop control system sends inputs into a process and produces an output, but it does not monitor or adjust based on the actual result. Such systems rely on predefined settings and human intervention to make corrections. In simple terms, an open loop assumes that the process will always behave as expected, even though real-world conditions can change.
A simple example of an open loop system is an electric kettle without a thermostat. Once switched on, it heats the water for a fixed time regardless of whether the desired temperature is reached.
By contrast, a closed loop control system monitors the output and uses a feedback system to adjust and maintain the set point. This capability allows it to adapt automatically to variations in conditions, delivering more accurate control and better energy efficiency.
One familiar specific application of a closed loop is in cruise control on a vehicle. The driver sets a speed (set point), and the system measures the actual speed continuously. If the vehicle slows down due to a hill, the controller increases the throttle to restore the set speed, conserving fuel and maintaining comfort without requiring constant driver input.
In illustration:
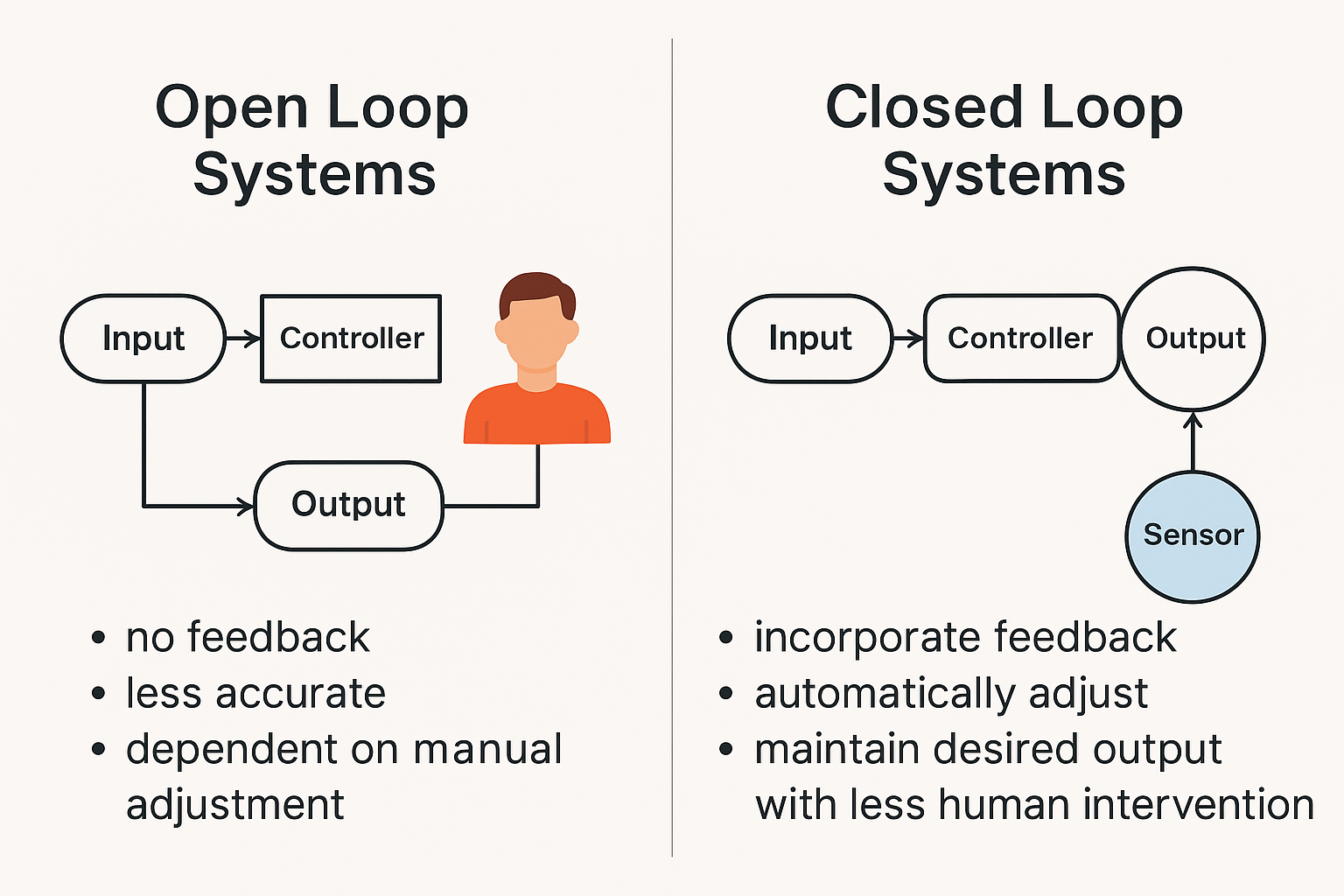
This distinction is crucial in selecting the right control loops for industrial applications and sustainability efforts.
Why Closed Loop Systems Matter in Industrial Applications
Closed loop systems are fundamental to achieving optimal performance, efficiency, and sustainability in modern industrial applications. They offer accurate control over critical variables such as temperature, flow, pressure, or chemical concentrations, ensuring that processes stay within desired limits.
In environments like manufacturing, power generation, and HVAC operations, small deviations in the actual temperature, flow rate, or other parameters can cause waste, equipment damage, or regulatory non-compliance. By continuously monitoring outputs and correcting discrepancies, closed loop systems reduce the need for constant human intervention and minimize the risk of costly errors.
In a heating system, for example, a closed loop can maintain a stable temperature while conserving energy, extending equipment life, and improving safety. Similarly, in such systems used for water treatment, feedback control ensures that chemical dosing stays within safe and effective ranges, reducing waste and protecting the environment.
These systems also contribute to energy efficiency by optimizing the use of raw materials and reducing waste materials. Their ability to self-correct promotes sustainability efforts by lowering carbon emissions, conserving natural resources, and minimizing the environmental impact of the production process.
Multi-Function Products in Closed Loop Systems
While a closed loop system offers advantages such as accurate control, energy efficiency, and reduced waste, maintaining and optimizing these systems still requires appropriate treatment strategies. This is where multi-function products become essential.
A multi-function product is a chemical formulation or material designed to perform several treatment roles at once within the loop system. Instead of using separate chemicals for each task, a single product combines multiple functions into one effective solution.
For example, a well-designed multi-function product can simultaneously:
- Inhibit corrosion to protect metal surfaces
- Prevent scale buildup that reduces heat transfer efficiency
- Control microbial growth to prevent fouling and health risks
- Buffer pH to maintain water chemistry stability
- Provide freeze protection for systems exposed to low temperatures
These products also support waste management and sustainability efforts. By simplifying the production process, they conserve natural resources, reduce the amount of raw materials used, and minimize waste materials generated. Using fewer containers, requiring fewer shipments, and occupying less storage space help reduce carbon emissions and improve the efficiency of the supply chain.
In a heating system or process cooling loop, applying a multi-function blend ensures these critical protections are in place without the complexity of managing several separate treatments. This reduces human intervention, lowers operational risk, and supports consistent optimal performance, even under challenging conditions.
Learn more on ETI’s custom blending and formulation service.
The Role of ETI’s Custom Formulations in Closed Loop Systems
Maintaining a closed loop control system is not a one-size-fits-all task. Each specific application has unique variables, including water chemistry, metallurgy, temperature ranges, and operational demands. This complexity requires more than off-the-shelf products. That is where ETI’s custom formulation expertise becomes invaluable.
ETI develops advanced, multi-function products specifically designed to meet the requirements of your loop system. These formulations are engineered to perform multiple control actions, reducing the number of products you need to maintain your system and simplifying your process.
How ETI Supports Closed Loop Systems:
- Assessment of Needs: ETI begins by analyzing the actual system, identifying the set point targets, system metallurgy, and water chemistry challenges.
- Development of Custom Products: Based on this assessment, ETI creates formulations tailored to your desired output, whether that is corrosion resistance, microbial control, or optimal heat transfer.
- Quality Control: Every formulation undergoes rigorous laboratory validation, ensuring the actual value delivered meets the intended reference input and remains stable under real-world operating conditions.
- Implementation Support: ETI provides guidance on feed systems, monitoring, and training to ensure optimal performance of the control loops.
By offering custom formulations, ETI helps you save time, lower costs, and improve system reliability while supporting your organization’s sustainability efforts and reducing waste. These solutions are designed to maintain your control system at peak efficiency, even in complex industrial applications.
Lean more about ETI’s chemical products for industrial water treatment providers.
How Multi-Function Products Support the Circular Economy
The concept of a circular economy focuses on designing processes and products to reduce environmental impact, conserve natural resources, and minimize waste materials by keeping resources in use for as long as possible. Multi-function products for closed loop systems directly support this approach.
Instead of relying on multiple single-purpose chemicals, a multi-function product combines several control actions into one formulation. This reduces the quantity of virgin materials needed, limits packaging waste, and cuts down transportation emissions along the supply chain.
For example, by using one advanced chemical that prevents corrosion, scale, and biological fouling, a facility can reduce its use of separate products made from virgin plastic containers, thus reducing reliance on newly extracted raw materials. When these products are packaged in recyclable or recycled plastic materials and applied efficiently, they help conserve resources while supporting sustainable waste management practices.
This also aligns with reusing materials wherever possible, extending the life of the system’s components, and lowering resource depletion. In addition, such practices contribute to reducing carbon emissions, saving resources, and meeting corporate sustainability efforts.
Creating Smarter, More Sustainable Closed Loop Systems
Understanding what is a closed loop system and its unique benefits is the first step toward optimizing your industrial operations. Closed loop systems deliver accurate control, energy efficiency, and reduced waste, making them indispensable for industries seeking to minimize environmental impact while maintaining optimal performance.
To fully unlock the potential of such systems, multi-function products play a crucial role. They simplify operations, conserve natural resources, and align with sustainability efforts, all while supporting the desired output of your process.
For facilities ready to improve efficiency, reduce resource depletion, and contribute to a circular economy, ETI’s custom formulations offer tailored solutions backed by decades of expertise.
For further information, or to discuss a specific application, contact ETI today and discover how we can help you create smarter, more sustainable systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a closed loop system and how does it work?
A closed loop system monitors its output and adjusts its input based on feedback, maintaining the desired output automatically without constant human intervention.
How does a closed loop control system differ from an open loop control system?
An open loop system operates without feedback and cannot correct deviations, while a closed loop control system uses feedback to maintain accuracy.
Why are multi-function products important in closed loop systems?
Multi-function products simplify operations, save resources, reduce waste, and improve efficiency by combining several treatment actions into one formulation.
How do closed loop systems help conserve natural resources?
They optimize the use of energy and materials, reduce waste, and minimize resource depletion by maintaining optimal operating conditions.
Can multi-function products reduce environmental impact?
Yes, by reducing virgin plastic use, cutting carbon emissions, and supporting sustainability efforts through efficient waste management and reusing materials.